Enterprise Malware Protection: How to Build the Ideal Security Stack

For cybersecurity teams, enterprise malware protection is much more complicated than finding a needle in a haystack. Why? There is no single cybersecurity product or solution that provides all the features necessary to defend against the whole threat landscape.
What about Zero Trust, you ask? Nope. In fact, just what a Zero Trust strategy constitutes isn't universal! Learn more in our on-demand webinar, "Zero Trust: The Most Overused, Misused, & Abused Cybersecurity Term Today" by clicking the banner:
Instead of looking for the perfect tool, cybersecurity teams have to assemble a toolkit: a set of products and solutions that work together to provide robust threat protection, containment, mitigation, and remediation. This article is your guide to architecting that security stack. It will help you navigate enterprise malware protection solutions and select the tools that will maximize your network’s security profile.
For more on ensuring your network security, check out our guide, Malware Protection: Everything IT Pros Need to Know.
Jump to a section…
What Is Enterprise Malware Protection?
Solutions for Preventing the Compromise
Endpoint Security, Detection, and Response
Solutions for Containing and Mitigating Threats Post-Compromise
Cyber Monitoring and Analytics
Implementing Enterprise Malware Protection
What Is Enterprise Malware Protection?
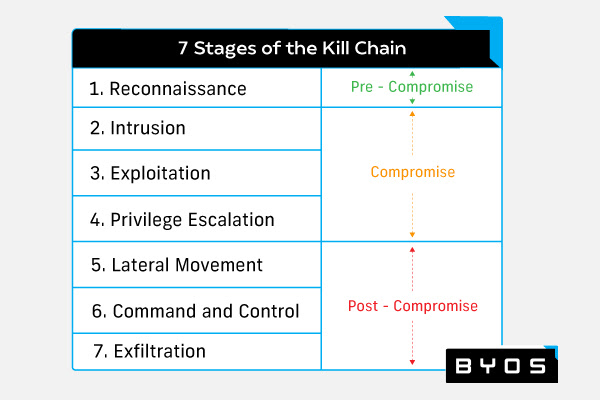
Enterprise malware protection is a multi-component cybersecurity solution that defends a network from malware and the full spectrum of cyber threats. A comprehensive enterprise malware protection system must counter six of the seven stages of the cyber kill chain. These stages are:
- Reconnaissance: The malicious actor assesses the target and determines the attack strategy.
- Intrusion: The malicious actor gains access to the target system using the attack strategy developed in the reconnaissance phase.
- Exploitation: The malicious actor sinks their claws into the target system and achieves greater access.
- Privilege escalation: The malicious actor gains admin privileges to maximize their access to the target system.
- Lateral movement: The malicious actor begins leapfrogging from system to system in the target network.
- Command and control: The malicious actor achieves network access.
- Actions on objectives: The malicious actor begins stealing, destroying, or encrypting target data.
Cyber security teams often need to use various enterprise malware protection tools to counter the cyber kill chain. We sort these tools into two major buckets: compromise prevention solutions and compromise containment and mitigation solutions.
We will provide a detailed breakdown of those tools later in this piece. First, let us look at what these solutions are up against.
The Rise of Ransomware
The prevalence of ransomware attacks has exploded in recent years. The most notable include 2020’s Hades ransomware attacks, the infamous Darkside ransomware attacks that shut down the Colonial pipeline in May 2021, and the Houston Rockets ransomware attack the month before. These cases are concerning in and of themselves, but the broader picture is even more worrisome. Between 2017 and 2020, Ransomware attacks increased by 65%, from 184M to 304M.
Unfortunately, many networks are currently vulnerable to ransomware attacks. As the Hades ransomware incident illustrates, networks relying on software alone to provide malware protection are unsafe. In that case, the malicious actors disabled the target organizations’ antivirus and endpoint detection & response (EDR) solutions. The increasing sophistication of malicious actors means security teams need a comprehensive approach to threat mitigation.
Now, let us review the elements of a comprehensive enterprise malware protection solution as they relate to the cyber kill chain.
Solutions for Preventing the Compromise
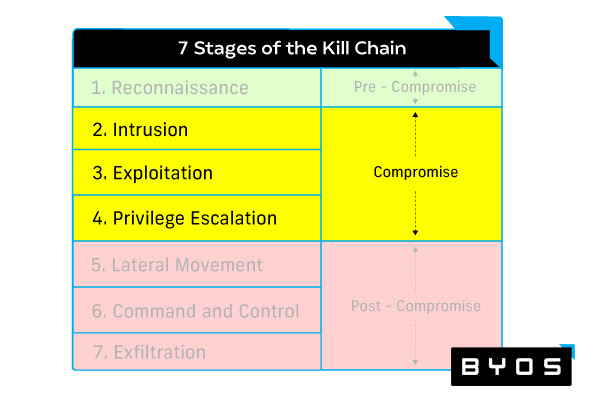
The enterprise malware protection tools in this bucket cover the intrusion, exploitation, and privilege escalation phases of the cyber kill chain. They attempt to manage user access, protect a network’s borders, mitigate vulnerabilities, and respond to an incident should one occur.
Identity Management
Identity management systems reduce the likelihood of an intrusion and make it much harder for malicious actors to escalate their permissions in the case of a compromise. To understand this solution space, we need to review two terms: identity and access management (IAM) and Zero-Trust network access (ZTNA).
IAM is a cybersecurity solution that oversees the relationship between users and technology resources. IAM solutions have two primary functions. The first is managing user credentials and permissions, which includes registering users, granting resource permissions, and the ability to issue temporary credentials. The second is verification when a user — or a malicious actor — requests resource access. This process involves analyzing user credentials and awarding the appropriate access given their permission profile.
ZTNA — a type of software-defined perimeter (SDP) — applies the Zero Trust framework to IAM. A ZTNA solution assumes that those trying to access technology resources have malicious intent and grants precision access to those resources through an encrypted tunnel. This tunnel blocks the user from discovering any aspect of a given resource or the broader network that has not been explicitly authorized. ZTNA is particularly effective for managing secure remote access.
Top vendors:
Perimeter Security
The premise behind perimeter security is simple: defend the walls of your castle. While perimeter security solutions help security teams pre-intrusion, the existence of a compromise means the system has failed its primary duty. Now, let us review the fundamentals of perimeter security and then take a brief look at the latest innovation in the space: next-generation firewalls (NGFW).
Perimeter security creates a barrier between your organization’s network and outside traffic — the internet. Perimeter security solutions prevent compromise via firewalls and spot it using intrusion detection systems (IDS). Fundamentally, firewalls weed out unwanted traffic. They usually perform packet filtering, network address translation (NAT), and Deep Packet Inspection (DPI). Firewalls also include virtual private network (VPN) support. On the other hand, IDS sounds the alarm if an intruder has made it past the firewall and lets security teams know it is time to take action.
NGFW represents the latest iteration of firewall technology. From VPNs to DPI, NGFWs have all the components of a traditional firewall. But NGFWs represent a significant improvement over previous generations by providing features like in-line deep pack inspect (DPI) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS). Just like an IDS, IPS continually monitors for indications of a breach; but, unlike IDSs, they can perform automated defense against those threats.
Top vendors:
Vulnerability Management
The purpose of vulnerability management tools is to find and fix your network’s weaknesses, thereby reducing the probability that a malicious actor will be able to compromise your network.
These solutions perform a variety of analytical operations to accomplish this goal. First, they must continually assess the size and shape of the evolving attack surface through real-time analysis. This means creating an accurate, real-time map of all the devices on your network and determining their risk profile by assessing all potential attack vectors. Second, these solutions need to gather and prioritize existing vulnerabilities according to the level of risk they represent. Third, they should suggest actions that the security team can take to reduce or eliminate the threat posed by the vulnerability.
Top vendors:
Endpoint Security, Detection, and Response
This category of compromise prevention solution aims to find and respond to an intrusion as quickly as possible to stop the spread, mitigate damage, and eliminate the threat. We will cover three categories of incident response solutions here: endpoint detection and response (EDR), managed detection and response (MDR), and extended detection and response (XDR).
EDR is an endpoint security solution that discovers suspicious activity, investigates alerts, uncovers the root cause of a compromise, and brings an incident to resolution. EDRs leverage historical threat intelligence to spot previously seen threats and predictive analytics to identify novel attack patterns and unknown malware. Once a threat has surfaced, EDRs can contain and destroy it.
MDR is when an organization outsources part or all of its incident response workload. An organization may choose to replace or supplement their incident response capabilities via an MDR firm because they lack internal IR expertise, are short-staffed, or have too many incidents to handle.
XDR is the next generation of EDR that expands the monitored territory beyond endpoints to include the whole cyber landscape. This broader solution monitors everything from servers to security information and event management (SIEM) tools for potential compromise and presents the incident details in a unified view. XDR solutions also utilize machine learning (ML) and automation to perform rapid data analysis.
Top vendors:
Solutions for Containing and Mitigating Threats Post-Compromise
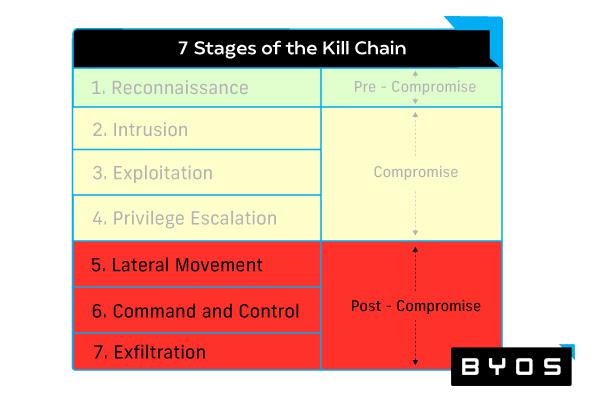
The following enterprise malware protection tools are concerned with stopping malicious actors from engaging in lateral movement, gaining command and control, and achieving their ultimate objectives. To do this, they provide robust analytics, endpoint-by-endpoint management, and the ability to shut off access to malicious actors trying to steal external assets.
Cyber Monitoring and Analytics
Cyber monitoring tools like SIEMs and user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) are about finding and stopping an attack in progress. By looking for abnormal patterns and evidence of recurring behavior across the network, these tools empower alert security teams to keep a breach from escalating into a disaster.
A SIEM is a security analytics tool that collects and analyzes data across your enterprise to discover threats. SIEMs serve as a hub for all log data, sifting through the information to look for suspicious recurring patterns that may indicate a breach and the use of lateral movement across devices. SIEMs are also a centralized location for threat intelligence feeds, offering a unified view of the latest research. These tools also fire alerts to warn security teams of the possible breach so they can start an investigation.
SIEMs often leverage UEBA to aid in threat detection. UEBA analyzes historical behavioral data to create working models of average user and machine network activity. Using these definitions, UEBA can identify novel threats and assign a risk score based on the nature of aberrant behavior. In addition, SIEMs that integrate UEBA are capable of real-time threat detection.
Top vendors:
Microsegmentation
Microsegmentation is an approach to network security that can significantly improve the ability to prevent an attack and mitigate its effects. Microsegmentation divides the network into endpoint-specific subnetworks, dramatically reducing the attack surface. This approach means even if a breach does occur, the inherent structure of the network significantly limits the possibility of spread.
Microsegmentation tools also provide security teams with a high degree of endpoint visibility and control. Security teams can monitor all the ingress and egress traffic of all devices that have been micro-segmented, allowing them to detect lateral movement and immediately lock down an endpoint should it suffer compromise. They can then remotely patch and remediate the device — getting the endpoint back online without legwork or laborious rebuilds.
Because it provides comprehensive remote administrator control and secures remote access for users, microsegmentation is a particularly critical solution for organizations with a distributed workforce.
Top vendors:
Web Access Protection
Because modern work often extends outside an organization’s network, web access protection solutions help security teams maintain healthy relationships between users and their internet tools and resources. As external applications can be a vital storehouse of sensitive data, security teams must keep unwanted parties from gaining access. This is one of the critical ways these tools can help keep digital assets safe after an attack has broken through the walls.
Below we review important two categories of web access protection tools: secure web gateways (SWG) and cloud access security brokers (CASB)
SWGs are a security tool that provides users with protected access to the web. SWG enables security teams to enforce web usage policies, blocking content, and provide threat protection.
CASBs is essentially a specialized SWG that helps safeguard the relationship between users and cloud services. CASB enables security teams to understand how many cloud services an organization is using, assess the risk level of the usage, ensure usage is following established policy, and detect violations or suspicious behavior. CASB’s can identify when a threat comes from a cloud service provider or when a malicious actor is posing as a user to gain access to assets on a cloud application. The latter feature can help mitigate the impact of an attack post-compromise.
Top vendors:
Implementing Enterprise Malware Protection
Picking an enterprise malware protection solution is not about finding a magic bullet. No single tool or platform will provide comprehensive protection against the myriad — and exponentially increasing — threats that populate cyberspace. Instead of catching a unicorn, security teams must assemble a cohort of complementary tools that afford unique solutions covering the entire cyber kill chain.
For organizations looking to optimize their ability to contain attacks, mitigate damage, and remediate the threat, the Byos µGateway provides the most effective microsegmentation solution on the market. Enabling comprehensive remote control of any device within the fleet, the µGateway gives administrators the ability to neutralize lateral movement with a single click. Ready to learn more? Contact us to learn more today.

